By Chandrachud

Executive Summary
The advent of 6G technology promises a paradigm shift in the telecommunications industry, driven by unprecedented connectivity, ultra-low latency, and unparalleled scalability. As networks become increasingly complex, the demand for automation in managing these systems has reached a critical juncture. Zero-touch networks, powered by AI-enabled autonomous management, offer a transformative solution by enabling self-configuring, self-healing, and self-optimizing capabilities without human intervention.
This Article explores the pivotal role of AI in facilitating autonomous network management for 6G, emphasizing its potential to enhance operational efficiency, reduce costs, and deliver superior user experiences. Key technologies such as machine learning, reinforcement learning, and real-time analytics are examined, showcasing their ability to predict and resolve issues, optimize network traffic, and enforce dynamic policies.
The transition to zero-touch networks is not without challenges. Security concerns, including adversarial attacks on AI models and data integrity risks, must be addressed through robust AI-driven security mechanisms. Ethical considerations and regulatory compliance further underscore the need for transparent and trustworthy AI systems.
From a business perspective, autonomous network management offers significant value, including cost savings from reduced manual interventions, faster fault resolution, and new revenue streams through AI-driven insights. By adopting a proactive approach, telecom operators can position themselves as leaders in the 6G era, unlocking opportunities in emerging markets such as IoT, AR/VR, and smart cities.
This paper provides a comprehensive roadmap for preparing for zero-touch networks, blending technical insights with strategic recommendations. It is a call to action for telecom stakeholders to embrace AI-powered autonomy as the cornerstone of the next-generation telecom ecosystem.
1. Introduction
1.1 The Evolution of Telecom Networks
Telecommunications have evolved significantly, from manual operations in 2G and 3G to semi-automated systems in 4G and 5G. With the advent of 6G, networks are poised to achieve ultra-high speed, reliability, and energy efficiency, marking the transition to fully autonomous operations.
- 1G introduced basic voice communication
- 2G added digital voice and text messaging
- 3G brought mobile data
- 4G introduced high-speed internet
- 5G enabled new applications that require ultra-low latency and allowed for the roll-out of the ‘Internet of Things’, or smart devices.
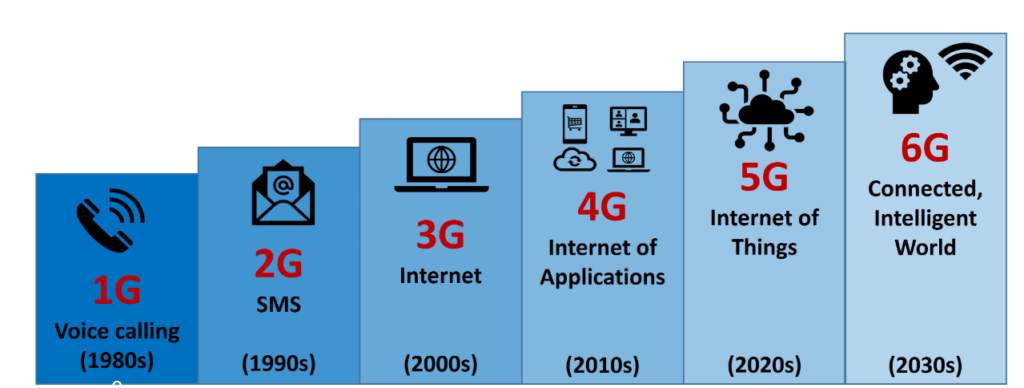
6G technology is anticipated to build on these advancements, promising a new era of wireless networks that cater to the increasing demand for high data rates and connectivity. The definition of 6G technology revolves around the idea of merging the physical, digital, and biological worlds, creating a hyper-connected – or ‘smart’ – society.
1.2 What Are Zero-Touch Networks?
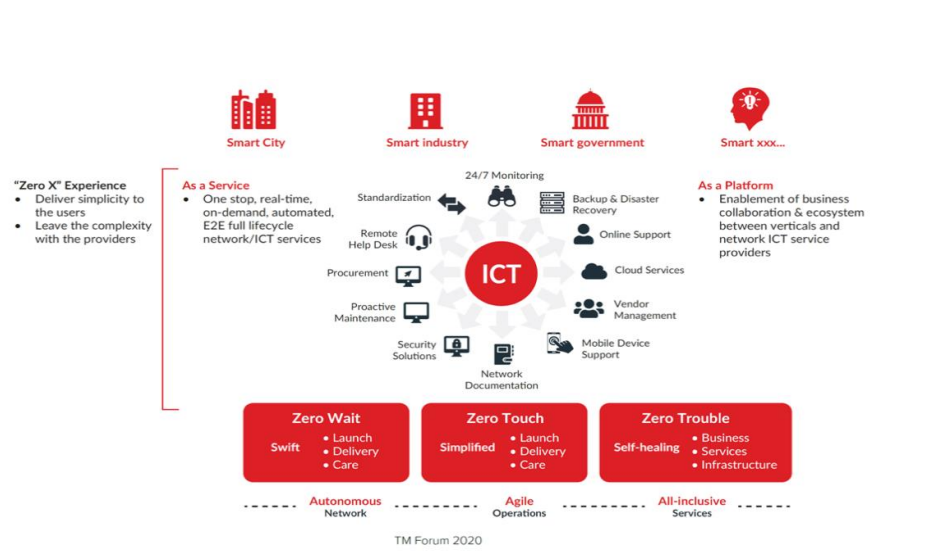
Zero-touch networks represent the epitome of automation, where AI enables networks to configure, monitor, and optimize themselves with minimal human intervention. These networks leverage AI-driven insights to ensure seamless operations, even under high complexity and dynamic conditions.
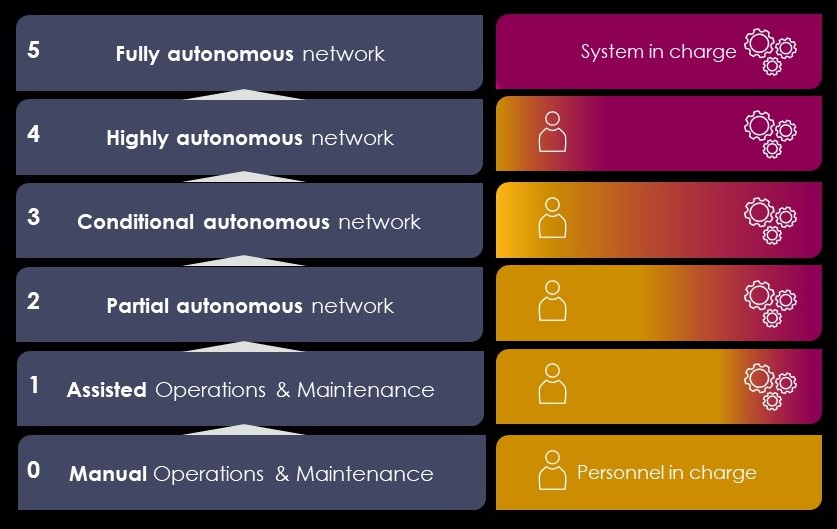
Autonomous levels (source: TM Forum)
Reference: ETSI Zero-touch Network and Service Management (ZSM) Framework, 2020.
1.3 Why Now?
- Increasing Complexity: Exponential growth in connected devices and traffic demands.
- Operational Challenges: Manual interventions are inefficient and error prone.
- Business Drivers: Pressure to reduce operational costs and enhance service quality.
2. AI in Autonomous Network Management
2.1 Key AI Technologies
- Machine Learning (ML): Predictive models for anomaly detection and capacity planning.
- Reinforcement Learning: Adaptive decision-making for dynamic network optimization.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Simplifying interactions between operators and AI systems.
AI in Autonomous networks (Source: TM Forum)
Reference: Sutton, R.S., & Barto, A.G. (2018). Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction. MIT Press.
2.2 Core Functions of Autonomous Networks
- Self-Configuring: Automated setup and deployment of network nodes.
- Self-Healing: AI-driven fault detection and resolution in real time.
- Self-Optimizing: Continuous performance tuning based on traffic patterns and service demands.
Case Study: China Mobile’s AI-powered network optimization system reduced latency by 30% in pilot deployments (Huawei White Paper, 2022).
2.3 The AI-Powered Network Lifecycle
- Setup: Automated resource allocation during deployment.
- Operation: Real-time monitoring and dynamic optimization.
- Decommissioning: Secure resource recovery and reuse.
3. Addressing Security in Autonomous 6G Networks
3.1 Security Challenges in Zero-Touch Networks
- Adversarial Attacks: Manipulating AI models to disrupt network operations.
- Data Integrity Risks: Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of real-time data streams.
- Automated Updates: Risks associated with self-deployed firmware and patches.
Reference: Goodfellow, I., et al. (2014). Explaining and Harnessing Adversarial Examples.
3.2 AI-Driven Security Mechanisms
- Anomaly Detection: Identifying unusual patterns in traffic or behavior.
- Adaptive Security Policies: AI-driven adjustments to combat emerging threats.
- Federated Learning: Secure training of AI models across distributed nodes.
3.3 Ensuring Trustworthy AI
- Transparency: Explainable AI models for accountability.
- Ethical Standards: Adhering to frameworks like IEEE’s Ethically Aligned Design.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meeting data privacy and security standards.
4. Business Impact and Opportunities
4.1 Operational Efficiency
- Reduced manual interventions lead to faster fault resolution and optimized performance.
4.2 Cost Savings
- Automation reduces operational costs by up to 40%, as demonstrated in early 5G trials.
4.3 Enhanced User Experience
- AI enables personalized service delivery and predictive maintenance, minimizing service disruptions.
4.4 Future Revenue Streams
- Monetizing AI insights through new offerings in IoT, AR/VR, and smart cities.
Reference: Ericsson Mobility Report, 2023.
5. Implementation Challenges and Mitigation Strategies
5.1 Technological Hurdles
- Scaling AI models for nationwide networks.
- Ensuring real-time processing without compromising accuracy.
5.2 Organizational Resistance
- Need for workforce upskilling.
- Addressing trust issues in autonomous systems.
5.3 Regulatory and Ethical Concerns
- Ensuring compliance with global standards like GDPR and CCPA.
Reference: GDPR Guidelines on AI, European Commission, 2021.
6. Future Outlook: The Path to Fully Autonomous 6G Networks
- Roadmap: Phased adoption of AI technologies, starting with semi-autonomous pilots.
- Partnerships: Collaboration between telecom operators, AI developers, and academia.
- Advancements: AI’s role in enabling real-time holographic communication and immersive experiences.
Reference: Nokia Bell Labs’ Vision for 6G Networks, 2024.
7. Conclusion and Recommendations
Zero-touch networks represent the future of telecom, combining AI’s capabilities with the unprecedented demands of 6G. By investing in autonomous management systems, telecom operators can achieve operational excellence, enhance security, and unlock new revenue opportunities. This paper serves as a guide for stakeholders to strategically embrace AI-driven autonomy, ensuring readiness for the transformative era of 6G.
8. References and Acknowledgments
- ETSI Zero-touch Network and Service Management (ZSM) Framework, 2020.
- Sutton, R.S., & Barto, A.G. (2018). Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction. MIT Press.
- Huawei White Paper: Autonomous Networks, 2022.
- Goodfellow, I., et al. (2014). Explaining and Harnessing Adversarial Examples.
- Ericsson Mobility Report, 2023.
- GDPR Guidelines on AI, European Commission, 2021.
- Nokia Bell Labs’ Vision for 6G Networks, 2024.
- Built In (2024). What Is 6G? Retrieved fromBuilt In
- Taoglas (2024). What Is 6G? All You Need to Know About 6G Technology. Retrieved from Taoglas
- TechTarget (2024). What is 6G? Overview of 6G networks & technology. Retrieved fromTechTarget
- tmforum.org
